In 2024 the global insurance and financial services market faced an unprecedented rise in cyber risks, lawsuits and regulatory requirements: according to Insurance Europe, losses from cyber incidents in the EU alone exceeded €8 billion, and the number of new insurance licences in Europe and Asia grew by 27% year‑on‑year. Against this backdrop, entrepreneurs and chief financial officers are under pressure: how to launch an international insurance product, protect assets, comply with Solvency II, reduce operating expenses and scale the business — all at once?
Why, despite hundreds of jurisdictions, are large and medium-sized companies increasingly choosing Malta Protected Cell Companies (PCC Malta) as a strategic tool for business growth and protection?
As the founder of COREDO, I see every day how regulatory, licensing and risk management issues become critical for our clients in Europe, Asia and the CIS. The Protected Cell Company structure in Malta is not just a fashionable trend, but a real way to address these challenges. In this article I will examine in detail what a Protected Cell Company is, how a PCC operates in Malta, what advantages it gives to business, and why registering a PCC in Malta right now is becoming a key solution for insurance and financial companies, as well as for projects in aviation, shipping and securitization.
Malta Protected Cell Company (PCC): what is it and how does it work?
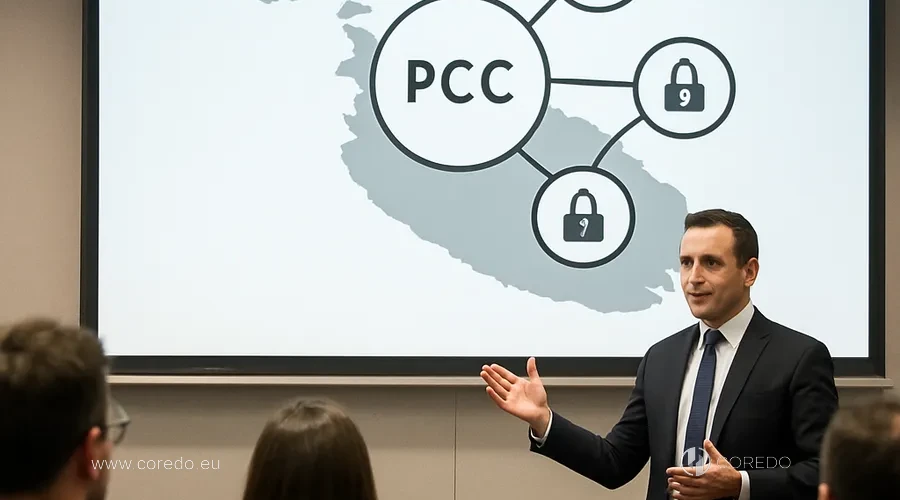

Malta Protected Cell Company (PCC): is a unique corporate instrument that allows creating separate cells (Cells) within a single legal structure, providing reliable segregation of each cell’s assets and liabilities. To understand how a PCC works in practice, it is important to grasp its basic setup: what the Core consists of and how the Cells are organized.
Structure of a PCC: what the Core and Cells are
Legal status of a PCC in Malta
The registration of a PCC in Malta is regulated by the Companies Act (Cap. 386) and the specialized rules of the MFSA (Malta Financial Services Authority). A Maltese PCC has the status of an independent legal entity, but each cell within the company is not a separate corporation; it is a structural part of the PCC with its own balance of assets and liabilities.
The process of registering a PCC in Malta includes:
- Preparing the constitutional documents specifying the ability to create cells.
- Obtaining preliminary approval from the MFSA for the structure and business plan.
- Contributing the minimum capital (usually from €100,000 for insurance PCCs, but requirements may vary depending on the licence and type of activity).
- Appointment of the board of directors and a compliance officer responsible for AML and corporate governance.
- Submitting the application for registration and licensing.
Thus, registering a PCC in Malta requires step-by-step preparation of documents, coordination with the MFSA and completion of all procedures in close interaction with the regulator, which, with a competent approach, takes from 2 to 4 months.
Next, we will consider the key asset protection mechanisms and the principles of ring-fencing in PCC structures.
Asset protection mechanisms and ring-fencing in PCCs
Benefits of PCC for businesses and insurance companies

The benefits of PCC for businesses and insurance companies open new opportunities for risk management, asset optimization and scaling operations. Thanks to its unique structure, a PCC allows not only to save on administrative expenses but also to flexibly develop a business within a single legal platform.
Cost savings and business scaling with PCC
Thus, the PCC model not only optimizes costs but also opens up wide opportunities for flexible management of insurance solutions and the implementation of captive insurance.
Flexibility in managing insurance products and captive insurance
Attracting investors and building trust in the business
Regulation and Licensing of PCC in the EU and in Malta

Regulation and licensing of PCC in the EU and in Malta are key factors that define how protected cell companies operate in the region. Special attention is paid to the licensing process and supervision by regulators such as the MFSA, which ensures compliance with European Union standards and Maltese law.
The role of the MFSA in regulating a Protected Cell Company (PCC)
Capital requirements under Solvency II
PCCs in Malta are required to comply with capital requirements set by both Maltese legislation and the European Solvency II directive. For insurance PCCs the minimum capital (Minimum Capital Requirement, MCR) starts at €100,000, but additional requirements may be imposed for individual cells depending on the nature of the risks and insurance products.
Licensing of PCC and individual cells
Licensing PCC Malta involves two stages: obtaining a license for the core and subsequent licensing of each new cell. To open a new cell it is necessary to submit a business plan, a risk description, the governance structure and to confirm the availability of sufficient capital.
Practical application of PCC in business
The practical application of PCC in business is becoming increasingly in demand due to the constant need for effective risk management, financial resilience and flexibility of corporate structures. The use of PCC is especially relevant for industries such as insurance and reinsurance, where the key tasks are risk diversification and capital optimization.
PCC in insurance and reinsurance
Malta Protected Cell Companies are widely used for insurance and reinsurance. Insurance cells allow the creation of bespoke products for corporate clients, managing the risks of individual projects or business segments, as well as operating through insurance intermediaries and brokers.
PCC in aircraft leasing and shipping
PCC Malta is actively used in the aviation and shipping business. Cells allow structuring the leasing of aircraft, marine cargo insurance and shipowners’ liability, providing transparency and asset protection.
Thus, the use of PCC provides a flexible structure for implementing complex tasks of managing and structuring transport assets, smoothly transitioning to the possibilities of applying cells in securitization and SCC.
Use of PCC in securitization and SCC
Corporate governance and risk management in a PCC

Corporate governance and risk management in a PCC provide a clear structure for allocating rights, responsibilities and control among shareholders, the board of directors and management, which is critical for the company’s resilience and operational effectiveness. This approach enables timely identification of risks and the design of internal processes so that they align both with business objectives and with requirements for transparency and accountability to stakeholders.
Corporate structure management and the board of directors
MFSA and Solvency II: reporting and disclosure
Each PCC and its cells are required to keep separate accounts, prepare individual financial statements and undergo an annual audit. The MFSA requires submission of regular reports on capital, risk management and financial results in accordance with Pillar III of Solvency II.
Legal risks when working with a PCC: how to minimize
PCC tax regime in Malta
The PCC tax regime in Malta provides international companies with unique opportunities to optimize their tax burden and manage financial flows. Thanks to a special approach to taxation and the flexible PCC structure, businesses can access a range of benefits, significantly reducing the effective tax rate and optimizing their operations.
Tax advantages of PCC for international companies
Registration and management of PCC – legal support
Recommendations for Entrepreneurs
Malta Protected Cell Companies are an effective tool for international business, allowing you to:
- Protect assets and isolate risks between business lines.
- Reduce operating costs and accelerate scaling.
- Attract investors through the transparency and manageability of the structure.
- Comply with the strict requirements of the MFSA and Solvency II.
- Optimize tax burden and simplify international settlements.
Practical steps to launch a PCC in Malta:
- Assess your business model and determine which lines require risk isolation.
- Prepare a business plan and PCC structure taking into account MFSA requirements.
- Appoint a board of directors and a compliance officer with insurance experience.
- Complete the registration and licensing procedures for the PCC and its cells.
- Implement an internal control system, automate reporting, and ensure Solvency II compliance.
For risk management and corporate governance use best international practices: regular audits, an independent board of directors, a transparent ownership structure and effective communication with the regulator.
If you plan to scale an insurance business, enter new markets or protect assets – a Malta Protected Cell Company will become your strategic advantage.